The Economist Intelligence Unit and the Alliance for Public Health presented a study based on research and modelling in Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and Russia. It is the first such study in the region, where researchers analyzed a number of possible scenarios and were able to get impressive findings.
The study points out that re-investing the total amount of € 12.34 billion saved from decriminalizing drug use in the four study countries (Belarus: € 431 million, Kazakhstan: € 773 million, Kyrgyzstan: € 38 million, Russia: € 11.1 billion) into scaling up antiretroviral therapy and opioid agonist treatment programs could help to effectively curb the HIV/AIDS epidemic in 20 years – with no need for additional public funds.
(Infographic source: The Economist)
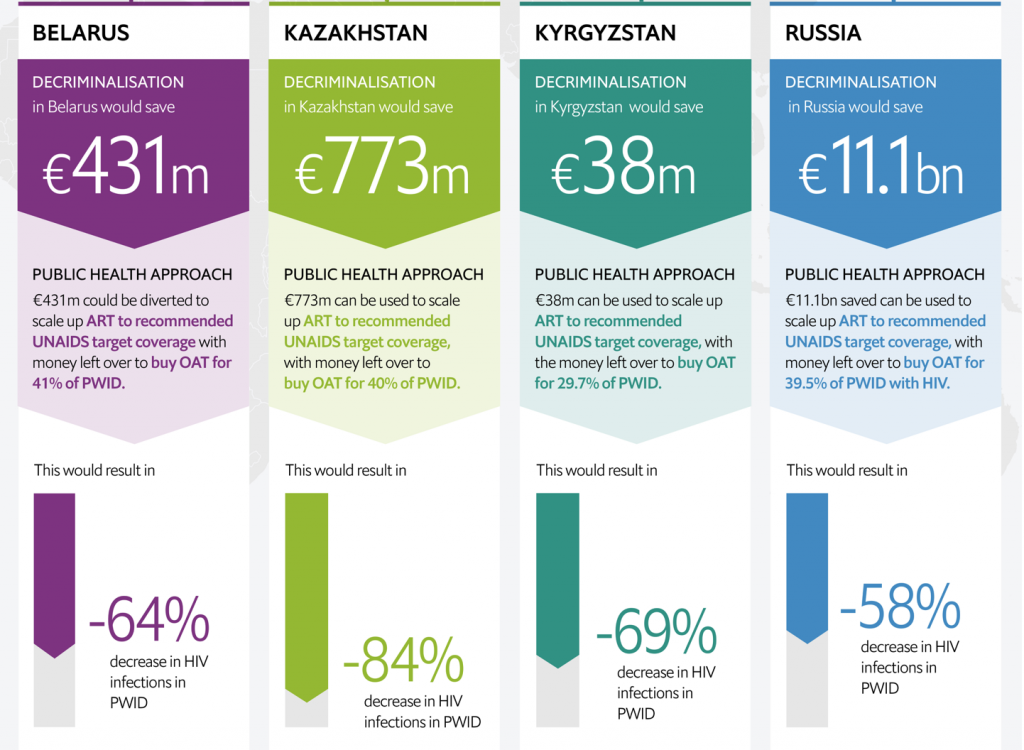 Doing so would, in turn, make a significant impact on the control over the epidemic in Eastern Europe and Central Asia (EECA) in general, with the following forecasted rates of averted HIV infections: Belarus – 64%, Kazakhstan – 84%, Kyrgyzstan – 69%, and Russia – 58%.
Doing so would, in turn, make a significant impact on the control over the epidemic in Eastern Europe and Central Asia (EECA) in general, with the following forecasted rates of averted HIV infections: Belarus – 64%, Kazakhstan – 84%, Kyrgyzstan – 69%, and Russia – 58%. The study findings are very timely, and the recommendations offered make the case for using such new approaches – especially given that the global targets relating to HIV/AIDS have not been achieved yet in these countries. “The previous UNAIDS target to halve HIV among [people who inject drugs] by 2015 was missed by a huge 80%. Continuing on this trajectory will mean also missing the more ambitious target to end AIDS by 2030,” states the report.
The study results clearly show the need to revise drug policy approaches in the focus countries, but the progress in this direction remains slow, said Dr. Chrissy Bishop, Senior Analyst for Health Policy and Clinical Evidence at the Economist Intelligence Unit. In this context, it is important to point out the cost-effectiveness of decriminalization approaches. Imprisoning people who use drugs is not only a huge burden to national budgets, but also further increases the number of new HIV cases.
The report also underlines that, because of competing needs, public health interventions for HIV have been low on the list of political priorities, with the allocation of domestic funds to scale-up HIV prevention programs falling far short of the needs. The authors of the study recommended that national governments should reconsider their approaches, because criminalizing people who use drugs does not make sense, compared to the provision of medical and social support.
“What is striking about these findings is that the savings can be achieved, and the HIV infections can be averted in the countries following a shift in resources from criminalization to HIV treatment and harm reduction,” underlined Dr. Bishop.
“This report has tremendous potential to be the basis of our future efforts. For the EECA countries it is very significant and can serve as a strong incentive to work even more to stop the HIV/AIDS epidemic, using all the possible arguments to advocate for the elimination of repressive drug policies,” pointed out Andriy Klepikov, Executive Director of the Alliance for Public Health.
Today, Eastern Europe and Central Asia is the only region in the world with catastrophic dynamics of the HIV/AIDS epidemic growth. Since 2010, the number of new HIV cases grew by 72%, while mortality increased by 24%. People who inject drugs account for nearly half of all new HIV cases in the region. According to 2017 data, in Russia alone there are 1.8 million people who use drugs.
Drug policies in the EECA countries are quite similar – characterized mainly by prevailing punitive measures, while public health measures aimed at prevention, rehabilitation, treatment, harm reduction and access to controlled medicines still have lower priority for national governments. The main victims of such an imbalance are people who use drugs – who become hostage to the existing approach as the efforts of the law enforcement agencies are predominantly aimed at them.
The authors of the study show that decriminalization, and the re-investment of the saved resources into the health sector to support harm reduction programs, will lead to between 17,800 and 2.6 million life years gained for people who inject drugs in the study countries.
It should be noted that one of the key recommendations presented in the report is to address stigma and discrimination: “Stigma and discriminatory attitudes towards vulnerable populations need to be stopped. Stigma-reducing workshops which educate the health and law enforcement sector on HIV prevention is a simple yet scarce solution in EECA. The importance of counselling, supporting positive mental health, addressing homelessness, preventing overdose and providing access to sexual and reproductive health services should be central to these educative workshops. Long term solutions require consistent and robust data collection on violence, discrimination and stigma, alongside actively using tools of influence such as shadow and alternative reporting to UN human rights treaty bodies”, states the report.
Catalyzing change
During the online presentation of the study results, international experts, law enforcers, researchers, civil society representatives and health professionals from the focus countries shared their comments. Participants from 20 countries watched the online discussions live.
When discussing the study report, speakers agreed that the findings are striking and can be used to advocate for the elimination of repressive drug policies in EECA countries. However, they pointed out that rapid change should not be expected. Michel Kazatchkine, member of the Global Commission on Drug Policy, assured that the economic justifications for alternative approaches – as presented in the report – can be used by UN agencies and national partners to advocate for change in the countries.
The report clearly shows how modelling can be a significant supportive tool to plan and develop government policies in the long-term. Results of such modelling studies are part of the evidence base, and this is an important consideration both for individual countries and for the region as a whole. Professor Kazatchkine underlined that it is very important that future drug policies should be based on cost-effectiveness and human rights, especially in Russia where there is a very strong political and ideologic opposition to harm reduction and opioid agonist treatment.
It should be noted that, as opioid agonist treatment is not available in Russia, “scaling up needle and syringe programs (NSP) is an alternative solution which would be cheaper… It would cost on average €46.5m per year to get 60% coverage of [people who inject drugs] and avert around 14,000 HIV infections per year. What is striking about these findings are the savings and HIV infections averted following such a simple shift in resources from criminalization to harm reduction approaches, something governments cannot ignore,” states the report.
Aleksander Kwaśniewski, Chair of the Eastern and Central European and Central Asian Commission on Drug Policy (ECECACD), gave the example of Switzerland. In the early 1990s, the country had the highest HIV prevalence among people who inject drugs, similar to what is happening in the EECA region today. The number of people injecting drugs was growing, they were marginalized by society and harassed by police. Despite having sufficient financial means, the Swiss government decided then to stop using repressive methods, but to initiate a massive scale up of harm reduction services. A large spectrum of treatment and support options was offered to people who use drugs, from rehabilitation to lifetime maintenance, to address the transmission of HIV and other infections. The results were rapid and astonishing. The HIV rate among people who inject drugs fell from 30% in 1993 to under 2% in 2009, while the number of overdoses decreased by 62%. The challenging situation that Switzerland had 20-30 years ago is now repeated in the EECA region, and we can address those challenges in a similar way, by revising the repressive drug policies and reinvesting resources in HIV treatment and harm reduction programs.
According to Peter Sands, Executive Director of the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, the study on EECA drug policies can really catalyze the change. Mr. Sands underlined that now it is a very important time to be talking about the HIV epidemic, especially as the top topics for discussion are still COVID-19 and vaccines. Those are the realities that the world is facing. However, it is crucial to speak about the effective measures to fight HIV/AIDS, and for people to remember that there are other health crises and that actually COVID-19 is making them much worse. “We need to get people to think differently. We can’t afford to do things which were ineffective or served as barriers to making progress. Now is the time to say – that didn’t work,” said Mr. Sands. It is clear that governments are facing a lot of challenges, but they cannot ignore the alarming dynamics of the HIV epidemic, especially if this issue can be addressed at no added cost, as clearly shown by the study’s findings.
In wrapping-up the online discussion, Andriy Klepikov told participants, “This report is something new. We have been talking about decriminalization for many years now. However, in this study we were not raising the question of decriminalization, we asked an open question: Where can the money come from, if there is no money? The Economist offered a clear answer to this question. In 20 years, about € 12 billion can be saved in four countries by introducing humane drug policies based on human rights and reinvested in HIV treatment and harm reduction programs, which are cost-effective. Further advocacy should be based on those arguments. It is only a start of a broad discussion. There are good practices in the countries, and we need to strengthen knowledge sharing. We invite representatives of all the stakeholders to join the dialogue and discuss the details of the advocacy strategy to be implemented in the countries. Millions of lives are at stake and now we know for sure the answer to the question how countries can bring the dynamics of new HIV cases under control without allocating additional resources.”